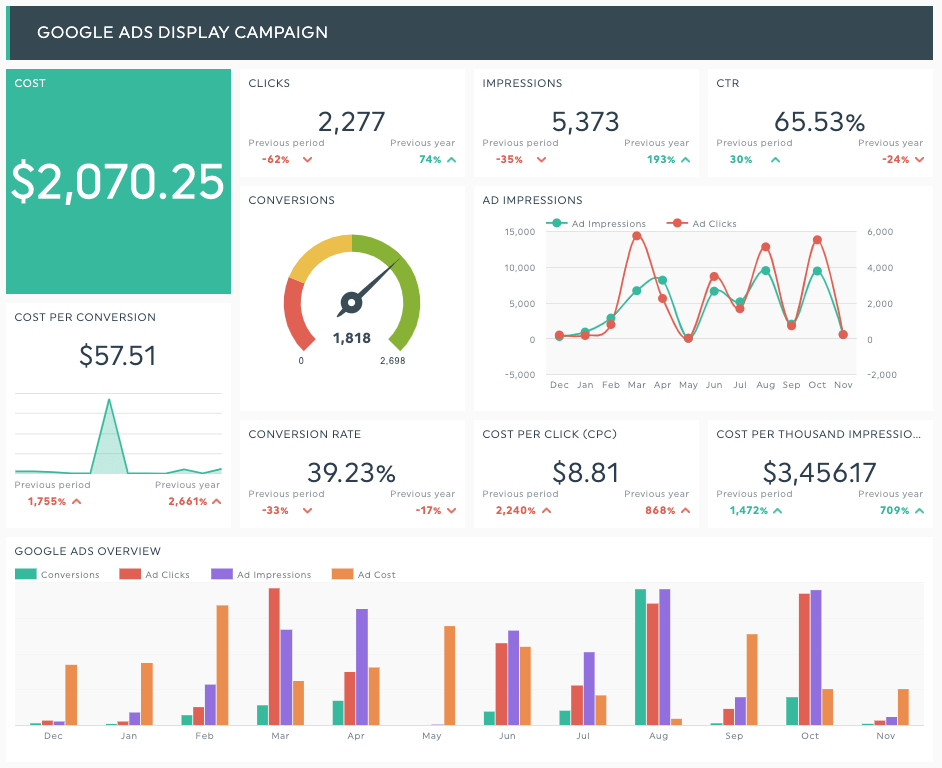
Performance marketing plays a crucial role in digital marketing and is often considered a key component of a comprehensive marketing strategy. It focuses on measurable and tangible results, allowing businesses to track, analyse, and optimize their marketing efforts based on performance metrics. Here are several reasons highlighting the importance of performance marketing in the digital landscape:
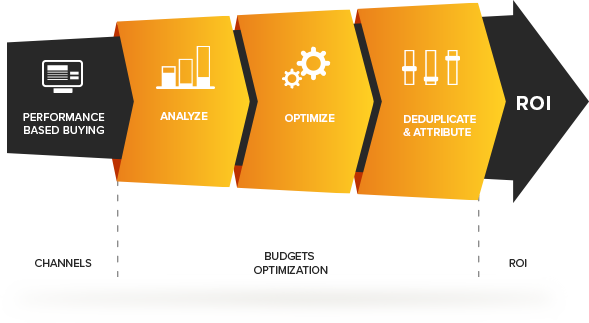
- Measurable Results:
Performance marketing relies on quantifiable metrics such as conversions, click-through rates, and return on investment (ROI). This emphasis on measurable outcomes allows marketers to assess the effectiveness of campaigns and make data-driven decisions. - Cost Efficiency:
By closely monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can optimize their marketing spend. Performance marketing allows for better allocation of resources to channels and campaigns that generate the highest returns, maximizing cost efficiency. - Targeted Advertising:
Performance marketing allows businesses to target specific audience segments based on demographics, behaviors, and interests. This targeted approach ensures that marketing efforts are directed toward individuals who are more likely to engage and convert. - Real-time Optimization:
Performance marketing enables real-time optimization of campaigns. Marketers can quickly identify what is working and what needs adjustment, allowing for immediate refinements to improve performance. - Flexibility and Adaptability:
In the dynamic digital landscape, trends and consumer behaviors can change rapidly. Performance marketing provides the flexibility to adapt strategies quickly, ensuring that campaigns stay relevant and effective in response to market shifts. - Attribution Modeling:
Performance marketing allows businesses to employ attribution models to understand the customer journey. This helps in identifying touchpoints that contribute to conversions, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the marketing funnel. - Cross-Channel Integration:
Digital marketing often involves multiple channels, such as social media, search engines, email, and display advertising. Performance marketing allows for seamless integration across these channels, ensuring a cohesive and synchronized marketing strategy. - Improved ROI Tracking:
Businesses can track the performance of each marketing channel and campaign accurately. This detailed tracking enhances the ability to calculate and improve the return on investment, making it easier to justify marketing expenditures. - A/B Testing and Experimentation:
Performance marketing allows for A/B testing and experimentation with various elements of campaigns, such as ad creatives, copy, and landing pages. This iterative process helps identify the most effective strategies for driving conversions. - Scalability:
Successful performance marketing campaigns can be scaled up to reach a larger audience or expanded to new markets. This scalability is advantageous for businesses looking to grow their online presence and customer base. - Customer Data Insights:
Performance marketing generates valuable customer data and insights. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns, businesses can refine their targeting strategies and create more personalized and effective campaigns. - Transparent Reporting:
Performance marketing emphasizes transparency through detailed reporting. This transparency fosters accountability, allowing businesses to clearly see the impact of their marketing efforts and make informed decisions.
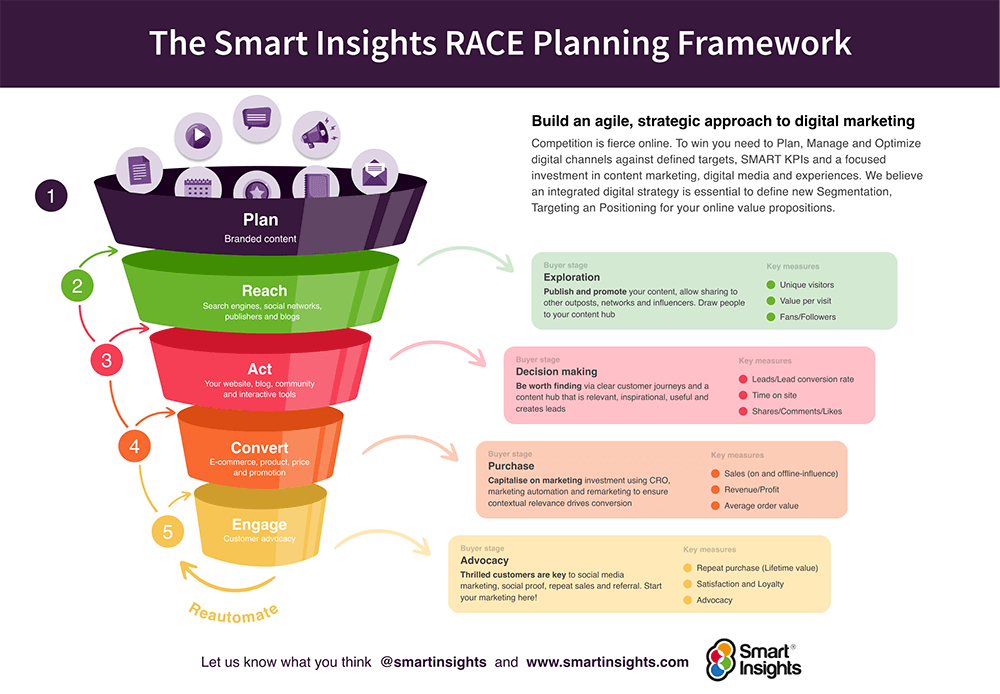
In summary, performance marketing is instrumental in driving results, optimizing marketing efforts, and achieving a strong return on investment in the digital space. Its emphasis on data-driven decision-making and measurable outcomes aligns well with the dynamic and competitive nature of the digital marketing landscape.
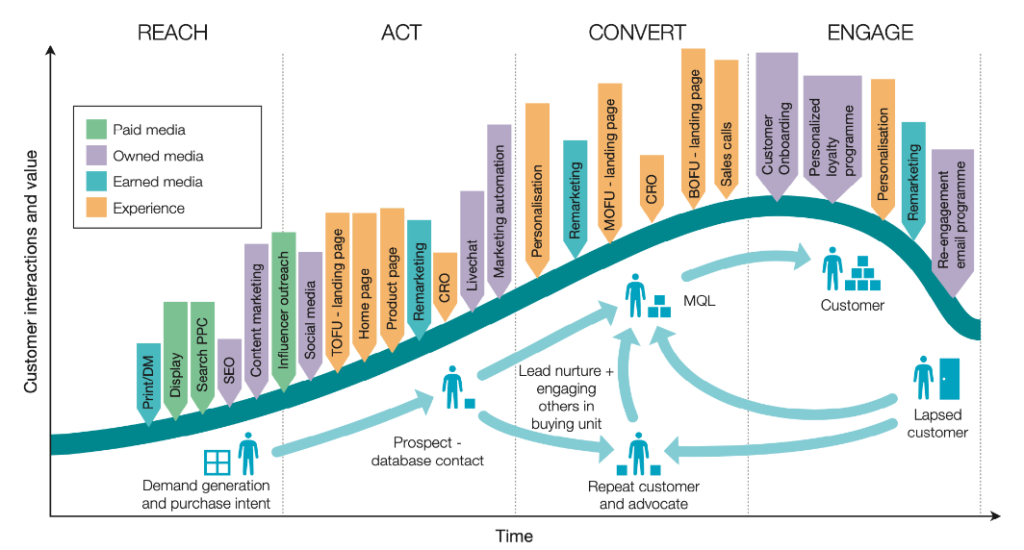
Performance marketing encompasses various terms and strategies, and PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is a key element within this digital marketing discipline. Here are some important terms related to PPC and performance marketing:
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click):
PPC is a digital advertising model where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It’s a way of buying visits to a website rather than earning those visits organically. - CPC (Cost-Per-Click):
CPC represents the actual price an advertiser pays for each click in a PPC campaign. It is calculated by dividing the total cost of the campaign by the number of clicks. - CPM (Cost Per Mille):
CPM is a metric that represents the cost of 1,000 impressions (displays) of an advertisement. It is often used in display advertising where advertisers pay for every 1,000 times their ad is shown. - CTR (Click-Through Rate):
CTR is the percentage of people who click on an ad after seeing it. It is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions and multiplying by 100. - Quality Score:
Quality Score is a metric used by search engines (e.g., Google) to measure the quality and relevance of your keywords, ad copy, and landing pages. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower CPC and better ad placements. - Ad Rank:
Ad Rank determines the position of an ad on a search engine results page (SERP). It is calculated based on the bid amount, Quality Score, and ad extensions. A higher Ad Rank increases the likelihood of a higher ad position. - Conversion Rate:
The conversion rate is the percentage of users who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form, after clicking on an ad. - ROAS (Return on Ad Spend):
ROAS measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. It is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the advertising cost. - Impression Share:
Impression share is the percentage of impressions your ads receive compared to the total number of impressions they could potentially get. It provides insights into the visibility of your ads. - Landing Page:
The landing page is the web page where users are directed after clicking on an ad. A well-optimized landing page is crucial for maximizing conversions. - Ad Extensions:
Ad extensions are additional pieces of information that can be added to a PPC ad to provide more details and encourage user engagement. Examples include site link extensions, callout extensions, and location extensions. - Bid Strategy:
Bid strategy refers to the approach or method used to set bids in a PPC campaign. Common strategies include manual bidding, automated bidding, and target CPA (Cost-Per-Acquisition) bidding. - Remarketing:
Remarketing (or retargeting) involves targeting ads to users who have previously visited your website but did not complete a desired action. It aims to re-engage and bring them back to the site. - Negative Keywords:
Negative keywords are terms that you exclude from your PPC campaigns to avoid triggering ads for irrelevant searches. This helps improve the relevance of your ads and reduces unnecessary clicks.
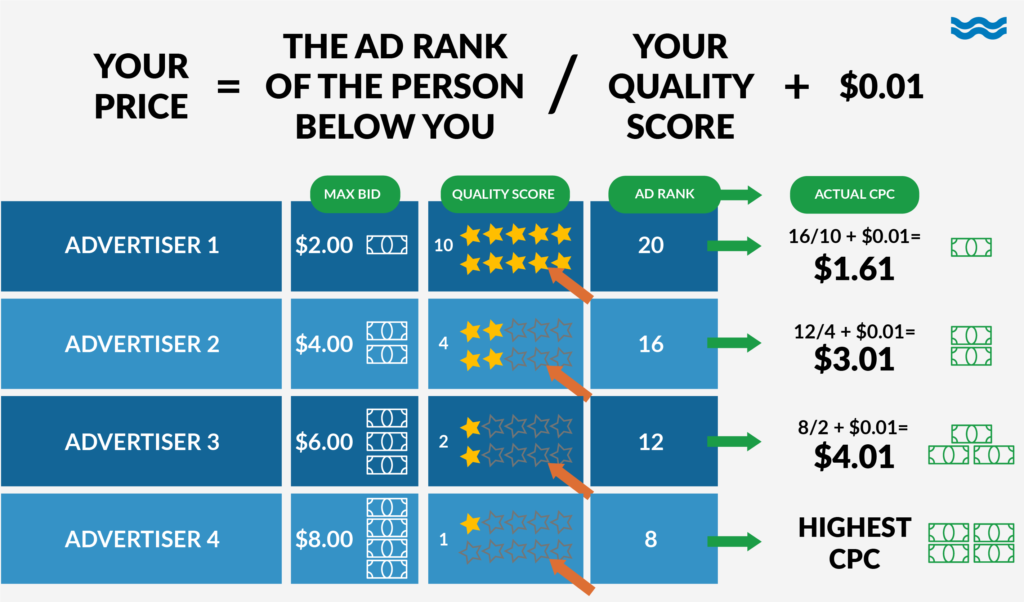
Understanding these terms and incorporating them into your performance marketing strategy can enhance the effectiveness of your PPC campaigns and contribute to overall campaign success.